How to Reverse ChangeNow & SimpleSwap.io Transactions
Cryptocurrency bridging platforms have gained significant popularity as they enable users to exchange different cryptocurrencies without using centralized exchanges (CEX). While their primary purpose is facilitating transfers between different blockchain networks, some users attempt to leverage these platforms to obscure their transaction history, making their wallet activities more difficult to trace.
However, the Odin team maintains advanced tracking capabilities that stay ahead of these obfuscation attempts. In this guide, we will demonstrate how to identify wallets that have recently received funds through bridging platforms and trace them back to their original source wallets.
For simplicity, we will focus specifically on Solana-to-Solana (SOL-SOL) exchanges, as analyzing cross-chain bridges involves more complex processes and requires additional time to investigate.
Understanding the Bridging Process
Before learning how to reverse-trace these bridging platforms, it’s essential to understand their operational workflow:
- Initial SOL Transfer: When bridging SOLANA to SOLANA, users must first send a specific amount to the exchange’s temporary wallet.
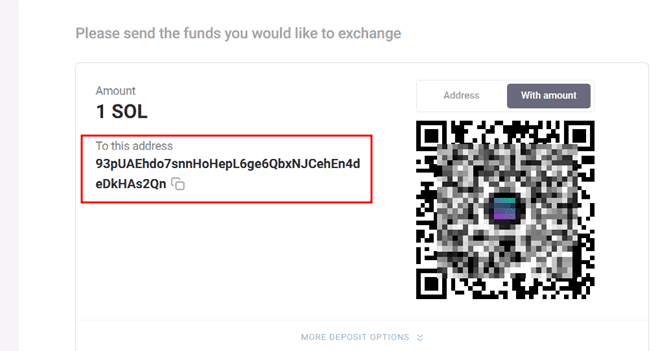
2. Temporary Wallet Operations The exchange uses a fresh temporary wallet for each transaction. These wallets have specific characteristics:
- They are newly created for each transaction
- They only handle receiving and withdrawing SOLANA
- The transactions occur in close succession
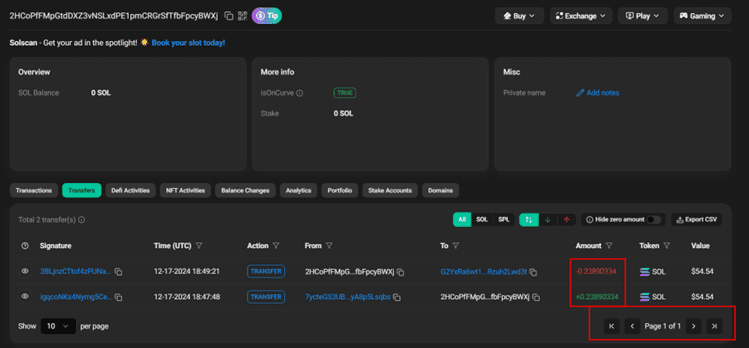
Also, note how the timestamps are very close, which is another indicator of these freshly made wallets.
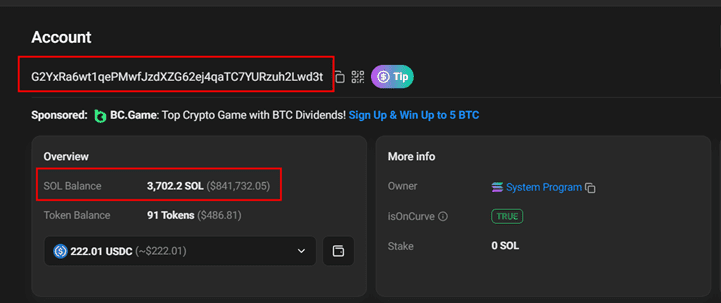
3. Main Wallet Transfer: The platform transfers funds from the temporary wallet to its main chain wallet. For SOLANA transactions, both Changenow and SimpleSwap use the same main wallet address: “G2YxRa6wt1qePMwfJzdXZG62ej4qaTC7YURzuh2Lwd3t”. This wallet exclusively handles SOLANA transactions.
As a summary, this is the workflow:
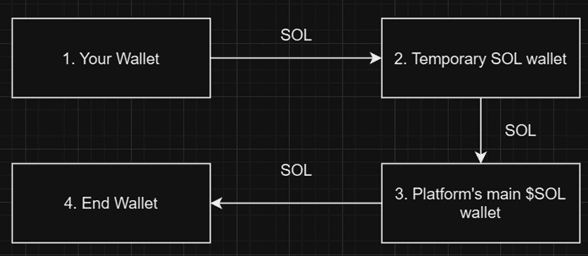
Reversing
Now that we understand the platform’s operations, we can trace transactions backwards. However, this technique is primarily effective for SOL-to-SOL transfers. Let’s examine both successful and unsuccessful tracing scenarios.
Successful case study
As an example of a wallet to reverse, we will take this one, which was funded by the exchange main solana wallet: 37d7AEne3KCgTzkEAAtYjuVDJTVwyVb5eEBz4WeLos8n
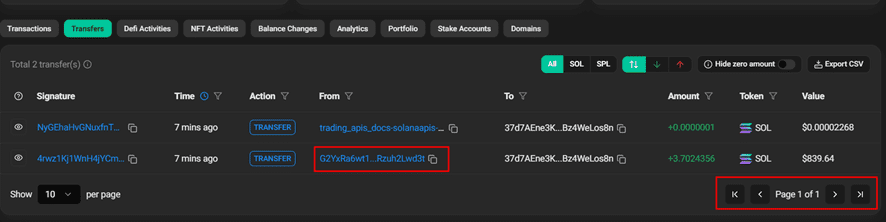
The transaction history shows that this wallet received funds from the identified main platform wallet (G2Y…d3t), which we previously established as the primary Solana wallet used by both ChangeNow and SimpleSwap.
To trace the original source, we analyze transactions in the main wallet matching the 3.70 SOL amount. This leads us to identify a corresponding incoming transfer from a temporary wallet with the same value, following the platform’s typical transaction pattern.
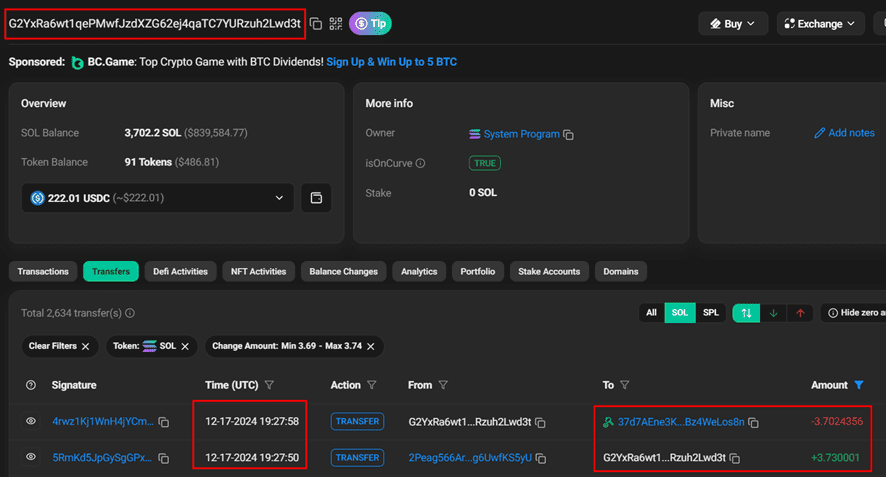
Analysis of the main wallet reveals a matching incoming transaction that occurred just 8 seconds before the outgoing transfer. This minimal time gap between transactions is a key indicator of a SOL-to-SOL bridge operation, as the platform processes these transfers almost immediately.
Having identified the temporary wallet (2Peag..5yU) involved in this transaction, we can trace back one step further to discover the original source of the funds.
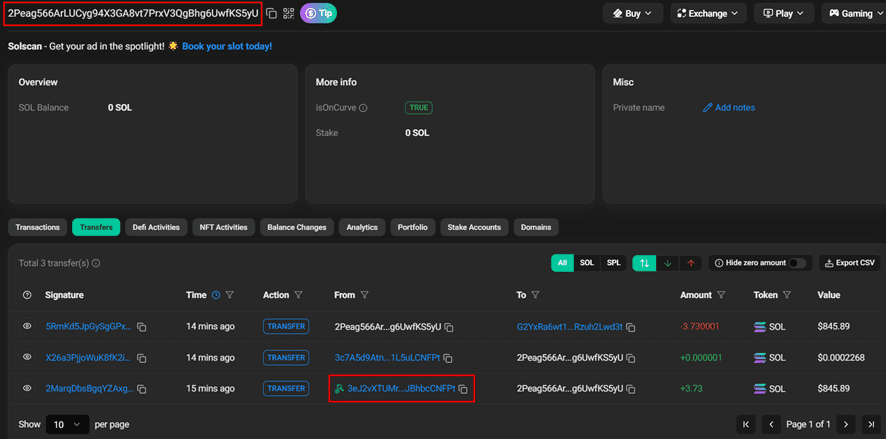
The transaction analysis reveals that the initial funds originated from wallet address 3eJ..FPt, which we can identify as the original source wallet. For reference, the complete wallet address is: 3eJ2vXTUMr3Tt8au2x9r2b8Quafc7eCYvbJBhbcCNFPt
Unidentifiable Case Study
While SOL-to-SOL bridge transactions can be effectively traced using the method described above, cross-chain transactions present significant challenges. When users bridge other cryptocurrencies to SOL, the tracing process becomes substantially more complex and resource-intensive, often making it impractical to pursue.
To illustrate this limitation, let’s examine wallet address: 33uvmRYEfJuFE7fE5iTsWzSPmL7aqkNuUrb5D9bhhz2v
This wallet received 3.72 SOL from the platform’s main wallet (G2Y..d3t), demonstrating a typical cross-chain bridge transaction pattern.
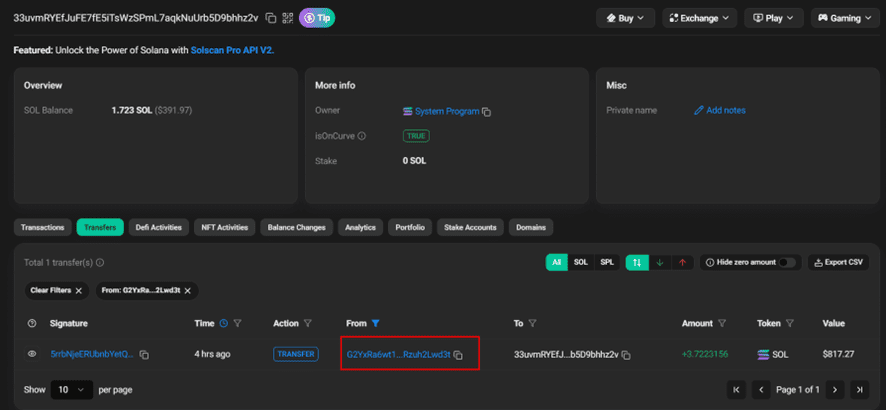
When examining the main platform wallet’s transaction history for corresponding incoming transactions of approximately 3.73 SOL, we find only the outgoing transfer. The absence of a matching incoming SOL transaction is significant for two reasons:
- It confirms this was not a SOL-to-SOL bridge transaction
- It indicates the incoming funds were in a different cryptocurrency before being converted to SOL
This asymmetry in the transaction pattern differentiates cross-chain bridge operations from the simpler SOL-to-SOL transfers we discussed earlier
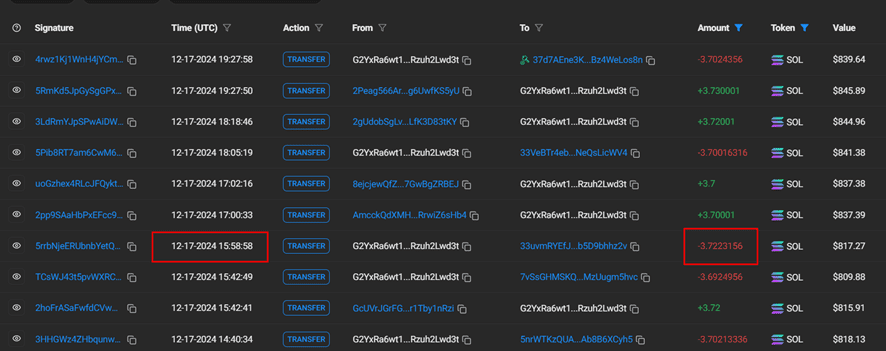
The significant time gap between transactions provides additional confirmation that this is a cross-chain bridge operation.
Additional Information
In the table below you can find the mother wallets of this exchanges based on the exchanged token. Note how SimpleSwap & ChangeNow have the same mother wallets.
| Token | Funding wallet Address |
| SOL | G2YxRa6wt1qePMwfJzdXZG62ej4qaTC7YURzuh2Lwd3t |
| TRX | TWS1onJnNTg8tJHomceqxBxTsUB1DHh7PV |
| BSC | 0xe2d60CFE3cF8B2079C7DF0144c5b28C03469775C |
| ETH | 0xEbA88149813BEc1cCcccFDb0daCEFaaa5DE94cB1 |
| BTC | bc1qq904ynep5mvwpjxdlyecgeupg22dm8am6cfvgq |
| USDC (ETH) | 0xD72CD83aFba0dCfEFf95D463adcB2b8dEf6aA623 |
| USDT (ETH) | 0xD72CD83aFba0dCfEFf95D463adcB2b8dEf6aA623 |
| USDT (SOL) | 2jwP4cuugAAYiGMjVuqvwaRS2Axe6H6GvXv3PxMPQNeC |
| USDC (SOL) | 2jwP4cuugAAYiGMjVuqvwaRS2Axe6H6GvXv3PxMPQNeC |

